The Flag Theory is a concept originally developed in the 1960s by Harry D. Schultz, a financial advisor and author. It revolves around a strategy to enhance personal freedom and achieve financial independence by strategically utilizing the benefits of different countries and legal systems. The core idea of the Flag Theory is to avoid being tied to a single country and instead leverage multiple locations worldwide to find the best conditions for taxes, legal protection, quality of life, and other crucial aspects.
The Original Three Flags
Initially, the Flag Theory consisted of three “flags” that should be strategically placed in different countries:
- Legal Residence (Flag 1): This is the country where one officially resides. It should ideally be a jurisdiction with no or very low taxes on income, especially income earned outside the country. Examples include Monaco, the Bahamas, or the United Arab Emirates.
- Business Location (Flag 2): This refers to the country where one conducts business or generates income. Ideally, it should be economically stable, offer a favorable tax environment, and be business-friendly. Countries like Hong Kong, Singapore, or Switzerland are often mentioned for this purpose.
- Asset Storage (Flag 3): The third flag concerns the storage and management of one’s assets. This should be done in a country that provides high security for investments and has strict banking secrecy laws. Switzerland, Liechtenstein, or Singapore are examples of such countries.
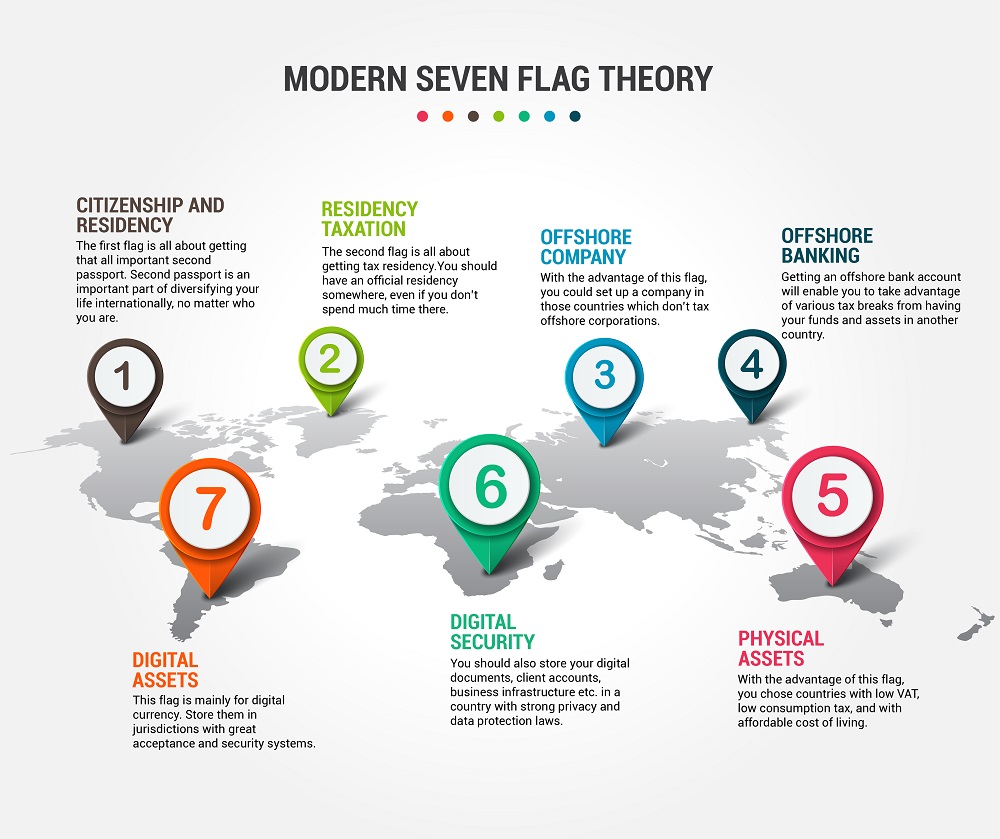
Expansion to Five or More Flags
Over time, the Flag Theory has been refined and expanded by other thinkers and financial experts. Nowadays, it often involves five or more flags:
- Second Citizenship (Flag 4): Many practitioners of the Flag Theory seek a second citizenship as insurance against political instability or legal issues in their home country. A passport from a country that allows visa-free travel to many nations is particularly valuable.
- Standard of Living (Flag 5): This flag represents the location where one actually lives and spends their time. Ideally, it should offer high quality of life, pleasant climate, and a desirable lifestyle, such as Spain, Portugal, or Thailand.
Some proponents extend the model to include additional flags, such as digital infrastructure, to ensure optimal access to technologies and communication capabilities.
Benefits and Challenges
The Flag Theory offers numerous advantages, especially for individuals looking to maximize financial freedom and minimize tax burdens. It allows individuals to take advantage of the best offerings from different countries while designing their lives to align with personal needs and goals.
However, implementing the Flag Theory is not without challenges. It requires significant knowledge and resources to plan and execute such a lifestyle. It involves not only financial means to establish oneself in various countries but also a deep understanding of the legal and tax frameworks in each jurisdiction.
Conclusion
The Flag Theory goes beyond mere tax optimization; it is a comprehensive life strategy aimed at maximizing personal freedom and minimizing risks associated with political and economic changes. It is particularly suitable for affluent individuals, entrepreneurs, and digital nomads seeking high levels of flexibility and independence. While the execution may be complex and resource-intensive, the Flag Theory presents intriguing opportunities in a globalized world to take control of one’s life and position oneself optimally.
Sources:
- Wie die Flaggentheorie Deine Freiheit sofort maximiert
- FlagTheory.com
- Was ist die Flaggentheorie 3.0 und wie unterscheidet sich diese zur klassischen?